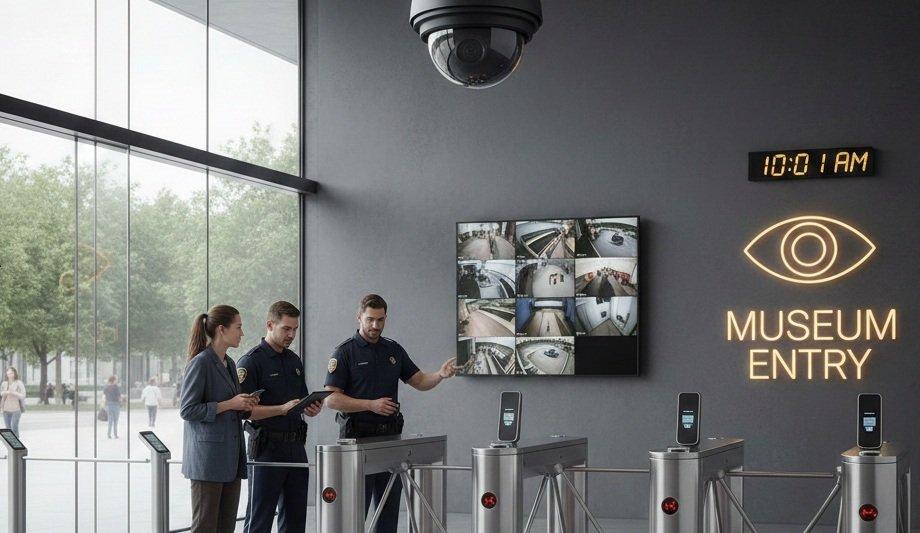
It took just seven minutes to steal more than $100 million in jewels from the Louvre, in an operation so swift and precise it exposed a deeper flaw in how even the most secure institutions protect what matters most.
It's reignited global scrutiny of both physical and digital security, revealing how gaps in coordination can turn sophisticated systems into operational failures.
Video intelligence and integrated monitoring
Across museums, government facilities, and corporate campuses, video security, analytics, and access control often operate in isolation. In the Louvre’s case, investigators later discovered that the only exterior camera near the Apollo Gallery was pointed west, leaving a point of entry completely unseen. Emerging video intelligence and integrated monitoring technologies show how unified systems could have changed the outcome by preventing the breach altogether or dramatically accelerating the investigation that followed.
As threats grow more sophisticated, so must the systems that defend against them. Disciplined system design, measurable performance standards, and continuous validation are what close security gaps. The Louvre incident highlights the industry’s shift toward a new expectation: security systems must not only capture video but understand context, anticipate failure points and maintain reliable performance under real-world conditions.
From blind spots to comprehensive awareness
Modern systems combine wide dynamic range, infrared and low-light capabilities, and flexible mounting designs
Fragmented visibility and weak system governance often create the very conditions that allow sophisticated breaches to occur, where technology can exist, but coordination, oversight, and accountability often fall short. A high-performing perimeter begins with quantifiable coverage targets — field of view, redundancy thresholds, and camera utilisation rates — rather than assumptions about what “should” be visible.
Modern systems combine wide dynamic range, infrared and low-light capabilities, and flexible mounting designs to ensure 24-hour situational awareness, even in visually complex environments like the Louvre. When combined with redundant recording and cross-camera correlation, these features ensure that even if one device is compromised or obstructed, others maintain continuous visibility.
The result is a perimeter with resilient coverage. Systems should be engineered to maintain visibility under failure conditions, measure performance against predefined KPIs, and surface anomalies automatically.
Intelligent detection and real-time response
Advanced analytics would have recognised the Louvre intrusion sequence as it unfolded. For instance, detecting the window breach, identifying unauthorised movement, and immediately notifying on-site security. What became a seven-minute heist could instead have been a single, automated alert cycle.
These systems interpret what’s happening by reading patterns of movement, environmental cues, and timing. They learn to tell the difference between ordinary activity and something that’s off. Here’s how that works in practice:
- Unauthorised Access Detection: Spots break-ins or forced entry by recognising sudden motion or environmental changes that don’t match normal use, like a window opening when it shouldn’t.
- Loitering and Suspicious Behaviour Recognition: Flags individuals lingering too long near restricted areas, giving security teams an early signal to check in before a situation escalates.
- Abnormal Motion Tracking: Picks up on unusual movements like running, erratic pacing, or carrying hidden objects.
- Object and Intrusion Differentiation: Knows the difference between a person and a passing shadow, cutting down on false alarms triggered by lighting shifts or reflections.
- Real-Time Alerts and Escalation: Sends instant notifications to control rooms or mobile devices so teams can coordinate a response within seconds.
Together, these capabilities shift security from passive recording to active interpretation, enabling faster decision-making that can be measured, refined, and validated over time.
Cybersecurity: The overlooked layer of physical security
The foundation of strong digital power lies in protecting the technology that protects everything else
Investigators later discovered that the Louvre’s security system was protected by the password: “Louvre.” It’s a reminder that even the most sophisticated physical security system can be undone by the weakest digital link.
A state-of-the-art camera system or motion sensor grid can underperform if the software is exposed or improperly managed. The foundation of strong digital governance lies in protecting the technology that protects everything else.
Cybersecurity: Defences and system access controls
- Protection of the security system itself. One of the most fundamental defences is enforcing robust credentials and multi-factor authentication for every user. Many organisations still rely on static passwords or shared logins for convenience, leaving systems vulnerable to both external intrusion and insider misuse. Multi-factor authentication ensures that even if a password is stolen, attackers can’t gain access without a verified secondary factor. Whether that’s a physical token, mobile verification, or biometric check. For security operations centres, where access often extends across multiple facilities or cloud environments, this extra layer can mean the difference between a minor attempt and a full-scale breach.
- Vetted system administration management. Another equally important defense is the establishment of tiered administrative privileges. Not every user needs full access to system configurations, live feeds, or stored recordings. Limiting permissions based on role and responsibility not only reduces the potential impact of human error but also minimises the damage if an account is compromised. Tiered access also introduces operational accountability, ensuring that sensitive functions, such as disabling cameras or altering detection zones, are limited to authorised personnel and subject to approval of workflows.
- Secure audit trails. Comprehensive audit logging is what brings digital oversight and accountability full circle. Every access attempt, system change, and data export should be recorded, timestamped, and monitored for anomalies. When properly implemented, audit trails not only support investigations after an incident but can also serve as early warning systems for suspicious behaviour. Automated alerts tied to unusual access patterns or repeated failed login attempts can prevent breaches before they escalate.
Integrating these principles aligns physical security with modern cybersecurity standards, ensuring resilience against both external and insider threats.
Future designs for resilient security
High-profile cases like this year’s security breach at the Louvre rarely stem from a single flaw. They arise from the absence of integrated oversight and collaboration between physical, digital, and operational layers.
The path forward lies in a unified model of security that blends comprehensive coverage, intelligent analytics, and secure system governance into a continuous, adaptive framework. When these elements work together, institutions can evolve from reacting to incidents toward anticipating and preventing them.
Again, as threats grow more sophisticated, so must the systems that defend against them. Whether protecting cultural landmarks, critical infrastructure, or enterprise environments, the future of video security must anticipate, protect, and build trust by design.
Discover how AI, biometrics, and analytics are transforming casino security